Berberine for HP bacteria is gaining attention as a promising natural remedy against Helicobacter pylori infections. This compound, extracted from various plants, has demonstrated remarkable antibacterial properties that can help manage and eradicate this troublesome bacteria, which can lead to serious health problems such as ulcers and even gastric cancer. In this article, we will explore the benefits, mechanisms, and applications of berberine in the treatment of HP bacteria, offering insight into its potential uses in modern healthcare.
Understanding Helicobacter Pylori and Its Impact on Digestive Health
Helicobacter pylori, often abbreviated as HP, is a spiral-shaped bacterium that resides in the lining of the stomach. It is estimated that more than half of the world’s population is infected with this microorganism. While some people remain asymptomatic, others may experience severe digestive problems, leading to conditions such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Let’s delve into what makes HP bacteria so concerning.
The Biology of Helicobacter Pylori
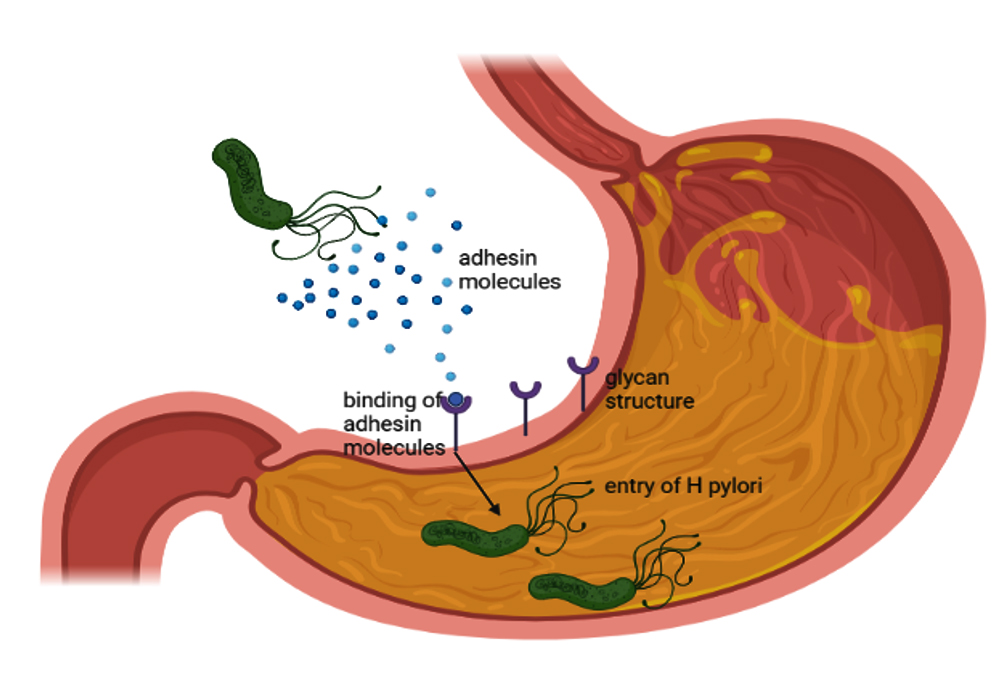
HP bacteria are uniquely adapted to survive in the harsh, acidic environment of the stomach. They possess flagella that help them navigate through the mucus layer that lines the stomach, allowing them to colonize and thrive. This ability not only contributes to their persistence but also plays a role in triggering inflammatory responses that can damage the stomach lining.
Furthermore, HP’s metabolic processes allow it to use urea as an energy source, enabling it to convert urea into ammonia, which neutralizes stomach acid. This creates a more hospitable environment for the bacteria while simultaneously increasing the acidity of the surrounding areas, leading to a higher risk of ulcer formation.
Symptoms and Complications Associated with HP Infection
While many people harbor the HP bacteria without noticeable symptoms, those who experience problems may face:
- Abdominal Pain: Often described as a burning sensation in the upper abdomen, this pain can occur shortly after eating.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Chronic infection can contribute to feelings of nausea and episodes of vomiting, particularly after meals.
- Bloating and Gas: Many people report increased bloating and gas production, exacerbating the discomfort.
Chronic HP infections have been linked to more serious conditions, including peptic ulcers, which can cause significant bleeding or perforation if left untreated. Additionally, researchers have established a connection between long-standing HP infection and gastric cancer, making it crucial to address this infection early.
Current Treatment Approaches for HP Bacteria
Traditional treatment methods typically involve a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). This “triple therapy” seeks to eradicate the bacteria while also reducing stomach acid to promote healing. However, antibiotic resistance has become a growing concern, leading researchers to explore alternative treatments such as berberine for HP bacteria.
This natural compound promises a dual-action approach: fighting the bacteria directly while supporting gut health. Let’s investigate how berberine fits into the picture.
Berberine’s Role in Managing HP Bacteria
Berberine is a bioactive compound found in several plants, including golden root and barberry. Recognized for its wide range of health benefits, recent studies have highlighted its specific antibacterial properties against HP bacteria. Let’s explore how berberine works within the body and its implications for HP management.
Berberine Mechanisms of Action
Berberine acts through multiple pathways, demonstrating its versatility as a therapeutic agent.
- Inhibition of Bacterial Growth: Research indicates that berberine canto inhibit the growth of HP bacteria by disrupting cell wall synthesis and interfering with metabolic processes. This direct antimicrobial effect helps reduce the bacterial load in the stomach.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: One of the most exciting aspects of berberine is its ability to modulate inflammatory responses. By decreasing cytokine production, berberine helps mitigate inflammation in the gastric mucosa, potentially alleviating symptoms associated with HP infection.
- Gut Microbiota Support: Berberine may encourage a healthier gut microbiome by promoting beneficial bacteria while inhibiting pathogens. This balance is crucial for maintaining a well-functioning digestive system and supporting overall gastrointestinal health.
Berberine’s multifaceted action makes it a strong candidate for further investigation as a stand-alone or complementary therapy in the management of HP infections.
Clinical Studies Supporting Berberine’s Efficacy
Several clinical studies have explored the efficacy of berberine against HP bacteria, yielding promising results.
- Study Results: In one study, participants treated with berberine alongside standard therapy exhibited higher eradication rates compared to those receiving conventional treatment alone. This suggests that berberine may enhance the effectiveness of antibiotics used to treat HP.
- Safety Profile: Another critical factor is the safety of berberine. Studies indicate that berberine has a favorable safety profile with minimal side effects when used appropriately. This makes it an attractive option for patients seeking alternative therapies that do not carry the risks associated with long-term antibiotic use.
As research continues, understanding the full spectrum of berberine’s potential will be essential to optimize its application in clinical settings.
Berberine Dosage and Administration
When considering berberine as a treatment option, understanding proper dosage and administration is vital to achieving optimal results.
- Recommended Dosage: Most studies suggest a dose range of 500 mg to 1500 mg per day, divided into two or three doses taken before meals. This ensures better absorption and maximizes its effectiveness against HP bacteria.
- Available Formulations: Berberine is available in several forms, including capsules, tinctures, and powders. Each formulation can vary in bioavailability, so it’s essential to choose a high-quality product that meets your needs.
- Consult with Healthcare Providers: Before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for those with existing health conditions or who are taking medications, consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial. Personalized medical advice ensures both safety and efficacy.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Berberine’s Effectiveness Against HP Bacteria
Along with using berberine for HP bacteria, adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve its effectiveness and overall digestive health. Integrating dietary modifications and stress reduction techniques can create a supportive environment for healing.
Dietary Considerations
What we eat plays a substantial role in our gut health and can exacerbate or alleviate symptoms related to PH.
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Including probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. These microorganisms can help restore balance in the gut and improve digestion.
- Fiber Intake: A diet high in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports healthy gut function and promotes a diverse gut microbiome. Fiber serves as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial bacteria and encouraging a robust digestive system.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce gastric inflammation caused byHP infection. Such dietary choices can complement berberine’s efforts to calm the stomach.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can negatively impact digestive health, exacerbating symptoms related to HP infection. Implementing stress reduction strategies is crucial.
- Mindfulness Practices: Engaging in mindfulness practices such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Creating a calming routine can positively contribute to gut health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise has numerous benefits that extend beyond physical well-being. Regular aerobic activity can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and positively influence intestinal motility, thus relieving digestive discomfort.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is paramount to maintaining overall health, including gut health. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and ensuring adequate rest can help regulate hormonal balance and support immune function.
By combining berberine for HP bacteria with these lifestyle changes, people can prepare for a more effective and holistic approach to managing HP infections.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions When Using Berberine
Although berberine shows promise as a treatment for HP bacteria, it is essential to recognize the potential side effects and precautions that should be considered.
Common Side Effects
Most people tolerate berberine well; however, some may experience mild side effects.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Diarrhea, constipation, or stomach upset may occur, especially if taken in high doses. Gradually increasing the dose may help mitigate these problems.
- Drug Interactions: Berberine may interact with medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate possible interactions.
Not Suitable for Everyone
Certain populations should be cautious when considering berberine.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established, so it is best to avoid berberine in these cases unless directed by a healthcare professional.
- People with Liver Conditions: Those with liver disease should consult their physician before using berberine, as it may affect liver enzymes and function.
Importance of Professional Guidance
Ultimately, working closely with a healthcare provider when incorporating berberine into your treatment plan is vital. They can offer personalized recommendations and monitor progress, ensuring safety and effectiveness throughout the process.
Frequently Asked Questions About Berberine for HP Bacteria
What is berberine and how does it work against HP bacteria?
Berberine is a natural compound derived from several plants known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It works against HP bacteria by inhibiting its growth and reducing inflammation in the stomach lining.
Can berberine replace traditional antibiotic treatment for HPV infection?
Although berberine shows promise as a complementary treatment, it should not replace prescribed antibiotics. Combining berberine with standard therapy may produce better results.
Are there any side effects associated with berberine supplementation?
Common side effects of berberine include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea or stomach upset. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help manage these issues.
How long does it take for berberine to show effects against HPV bacteria?
Results may vary, but many people may begin to notice more.Improvements within a few weeks of consistent use, particularly when combined with dietary and lifestyle changes.
Is berberine safe for everyone to use?
Not everyone should use berberine, particularly pregnant or breastfeeding women, and individuals with certain liver conditions. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, berberine for HP bacteria represents a promising natural remedy with significant potential to improve gastrointestinal health. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action against Helicobacter pylori, along with its ability to reduce inflammation and support gut flora, make it a strong candidate for further exploration in clinical settings. Combined with lifestyle modifications and dietary considerations, berberine offers hope for those seeking to effectively manage HP infections. As interest in natural remedies continues to grow, ongoing research will further illuminate berberine’s role in digestive health, possibly paving the way for innovative treatment options.


